World leaders rush to alleviate global supply chain disruptions
By France24
14 October 2021 |
12:44 pm
Officials are scrambling to help clear supply chain backlogs, with two of the US's largest ports operating 24 hours per day as traffic jams of container ships wait offshore. Also, the IMF unveils a new mechanism for rich countries to lend or donate to poor nations, and Hollywood braces for the biggest crew strike since the 1940s.
In this article
Related
April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
Related
15 Apr
Here's what's been making the business headlines in sub-Saharan Africa this week.
13 Apr
Nigeria’s Minister of Finance, Wale Edun says 4.83 trillion naira from T-Bills and Bonds issued in the first quarter of this year was used to pay part of the Ways and Means advances from the Central Bank of Nigeria. Sam Chidoka, CEO of Kairos Capital joins CNBC Africa for more on this discussion and Nigeria's debt management strategy.
4 days ago
A year after Lula came to power, his gamble has paid off: deforestation has been halved in the Amazon. But this success comes at the cost of sacrificing another ecosystem that's just as vital to Brazil: the Cerrado.
15 Apr
World leaders called for calm and an "utmost degree of restraint" in the aftermath of Iran's large-scale air attacks on Israel. Iran's attack, which involved the launch of more than 300 drones and missiles against military targets in Israel, has ratcheted up fears of a spillover conflict in a region already grappling with the ongoing Israel-Hamas war.
4 days ago
Some top Nigerian banks are eyeing the international and local capital markets to raise fresh capital in a bid to meet the recapitalisation exercise by the Central Bank of Nigeria. Egie Akpata, Chairman of Skymark Partners joins CNBC Africa to examine options available to banks.
2 days ago
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), a 10% rise in the dollar on the currency market would push down real gross domestic product (GDP) in emerging economies by 1.9% after one year, with adverse economic effects lasting more than two years
Latest
56 mins ago
Following the arrest of suspected left-wing terrorist Daniela Klette in Berlin, investigators are now hoping for new insights into crimes committed by the Red Army Faction.
56 mins ago
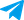
China's National Bureau of Statistics said on Monday that the country's economy grew to the tune of 5.3 percent in the first three months of the year, ahead of economists' expectations. Manufacturing and infrastructure are fuelling that growth, while housing and domestic consumption are still a source of concern. Meanwhile, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz is on a three-day visit to China, Berlin's top trading partner
56 mins ago
Maya Rudolph is back with a second season of her quirky billionaire workplace comedy, "Loot", while Oscar winner Robert Downey Jr dons multiple disguises for his role in the Vietnam War spy drama "The Sympathizer". Dheepthika Laurent and Olivia Salazar-Winspear also bring you the latest news from Canneseries, including Michael Douglas's historical drama "Franklin" and a biopic about Karl Lagerfeld.
3 hours ago
Scientists are testing a quadrupedal robot, named Spirit, in the rugged terrain of Oregon's Mount Hood, simulating the extreme conditions of the Moon and Mars.
3 hours ago
Can new laws against hate speech online also reduce harassment in the VTuber scene?
4 hours ago
Tunde Onakoya, a chess mastermind and founder of Chess in Slums Africa, has completed an incredible feat! He embarked on a journey to break the Guinness World Record for the longest chess marathon without a loss, aiming to surpass the existing mark of 56 hours and 9 minutes. And in the early hours of today, Saturday, April 20th, Tunde emerged victorious!
×

Get the latest news delivered straight to your inbox every day of the week. Stay informed with the Guardian’s leading coverage of Nigerian and world news, business, technology and sports.
















0 Comments
We will review and take appropriate action.